I am attempting to improve the performance of image resizing in C#. This StackOverflow answer provided some excellent pointers for improving performance.
I found these tips make a difference:
- Set pixel format to
PixelFormat.Format32bppPArgbwhen creating a Bitmap. - Set
Graphics.CompositingModetoCompositingMode.SourceCopy. - Set
Graphics.InterpolationModetoInterpolationMode.NearestNeighbor.
However, the last piece of advice reduces the quality when resizing. This is particularly bad when creating thumbnails.
So how do the different interpolation modes compare against each other in performance?
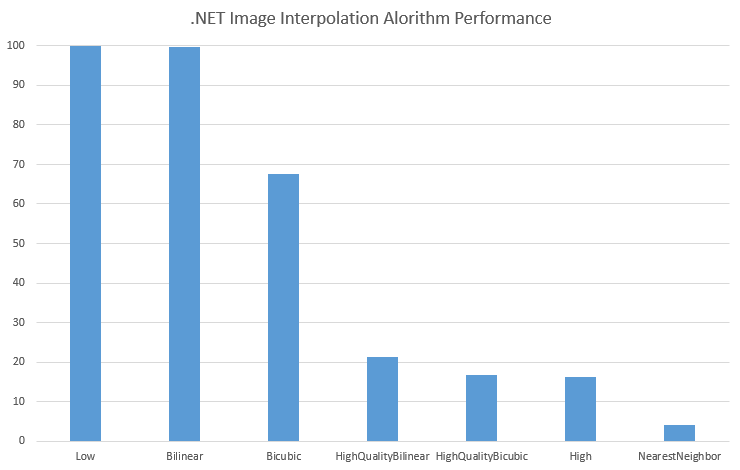
(lower is better)
But how do they compare in image quality? I have scaled an image to 10% of it’s original size using each technique (slowest first).
Low

Bilinear

Bicubic

HighQualityBilinear

HighQualityBicubic

High

NearestNeighbor

Conclusion
It seems to me that the sweet spot is anything starting with ‘High’. These seem to have a good enough quality, and an acceptable performance. The NearestNeighbor is really ugly, but if you want pure performance, or you’re not making a big difference to the scale, you might get away with it.
Image scaling source code
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thumbnail(InterpolationMode.NearestNeighbor);
Thumbnail(InterpolationMode.Bicubic);
Thumbnail(InterpolationMode.Bilinear);
Thumbnail(InterpolationMode.High);
Thumbnail(InterpolationMode.HighQualityBicubic);
Thumbnail(InterpolationMode.HighQualityBilinear);
Thumbnail(InterpolationMode.Low);
}
private static void Thumbnail(InterpolationMode interpolationMode)
{
using (var source = Bitmap.FromFile(@"C:\Users\Richard\Desktop\Windows10-wallpaper-img100.jpg"))
using (var target = new Bitmap(384, 286, PixelFormat.Format32bppPArgb))
using (var graphics = Graphics.FromImage(target))
{
graphics.CompositingMode = CompositingMode.SourceCopy;
graphics.CompositingQuality = CompositingQuality.HighSpeed;
graphics.InterpolationMode = interpolationMode;
graphics.DrawImage(source,
new Rectangle(0, 0, target.Width, target.Height),
new Rectangle(0, 0, source.Width, source.Height),
GraphicsUnit.Pixel);
target.Save($"{interpolationMode}.png", ImageFormat.Png);
}
}
}